Mast Climbers: Complete Guide to Vertical Access Equipment in Construction
Key Takeaways
Mast climbers are power-driven work platforms that move vertically along masts, classified as scaffolds under OSHA 29 CFR 1926.450(b) and ANSI A92
They provide safer, more efficient access than traditional scaffolding for facade work, carrying heavier loads to greater heights
Available in single or twin mast configurations with electric or combustion power options
Proper training, load compliance, and fall protection systems are critical safety measures.
Applications include masonry work, window installation, building repairs, and high-rise construction projects
The construction industry has witnessed a significant evolution in vertical access solutions over the past two decades. While traditional scaffolding has long been the standard for reaching great heights on construction projects, mast climbing work platforms have emerged as a superior solution for many applications. These innovative machines provide contractors with efficient access to building exteriors, combining enhanced safety features with impressive productivity gains.
Modern construction work demands equipment that can position personnel and materials at precise elevations while maintaining stability and safety. Mast climbers meet these requirements by offering high capacity transport platforms that can handle heavy loads and accommodate many trades simultaneously on a single structure. This comprehensive guide explores everything construction professionals need to know about these versatile access solutions.
What Are Mast Climbers?
Mast climbing work platforms are motorized vertical access equipment designed to transport workers, necessary tools, and materials along the exterior of buildings and structures. Unlike traditional scaffolding systems that remain static, these climbing work platforms move smoothly up and down vertical masts, providing precise positioning at any height.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) classifies mast climbers as scaffolds under 29 CFR 1926.450(b), meaning they must comply with specific scaffolding regulations and safety standards. This classification ensures that operators receive proper training and that equipment meets rigorous safety requirements before being deployed on any construction project.
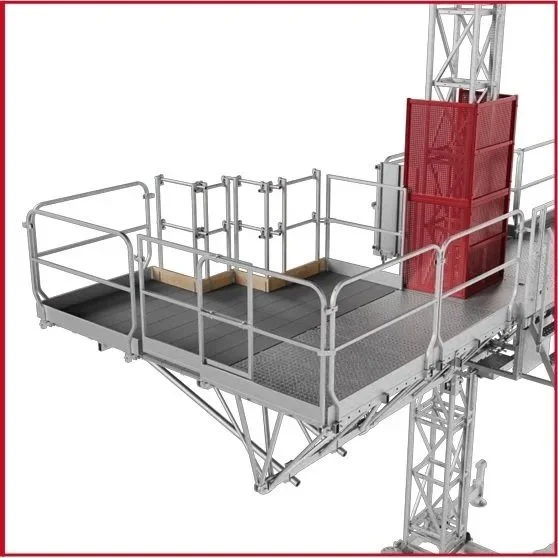
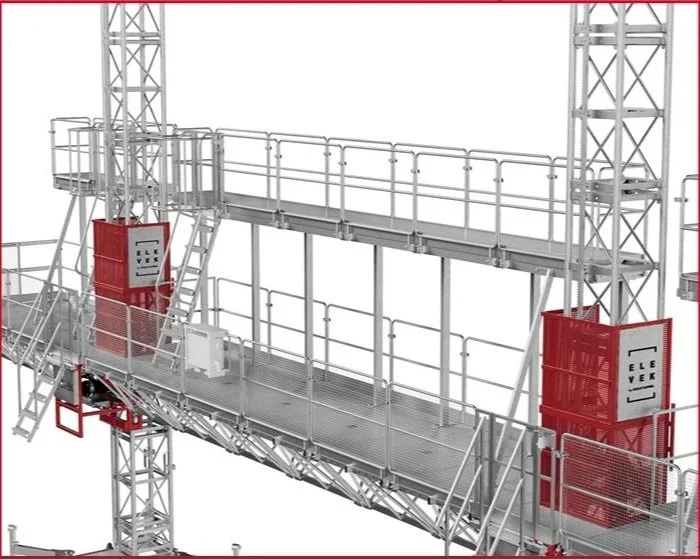
Core components of mast climbers include the vertical mast tower, which serves as the guide and support structure; the work platform, where personnel and equipment are positioned; the drive system that powers vertical movement; and a robust anchoring mechanism that secures the entire unit to the building structure. Each component is engineered to work together, creating a reliable solution for accessing exterior building surfaces.
How Mast Climbers Work
The vertical movement mechanisms in mast climbers rely on sophisticated hydraulic systems, electric motors, or mechanical drive systems that ensure smooth, controlled elevation changes. These systems are designed to handle the combination of platform weight, worker loads, and materials while maintaining precise positioning capabilities that construction work demands.
Mast tower construction begins with establishing a foundation that provides the support for the entire system. The tower sections are typically modular, allowing for easy assembly and the ability to reach varying heights depending on the specific requirements of each project. The foundation must be engineered to handle the loads generated during operation.
The platform attachment and guide systems ensure smooth vertical travel by maintaining proper alignment throughout the mast’s height range. These guides prevent lateral movement while allowing the platform to move efficiently up and down. The precision of these systems is crucial for maintaining stability when workers are performing detailed tasks like window installation or exterior finishing work.
Load distribution and weight capacity calculations are fundamental to safe operation. Engineers must consider the combined weight of the platform, workers, and all equipment to ensure the system operates within safe parameters. Most mast climbers can handle significantly heavier loads than traditional scaffolding, making them ideal for tasks requiring substantial amounts of materials or equipment.
Control systems and operator interfaces have evolved to provide intuitive, precise positioning capabilities. Modern units feature user-friendly controls that allow operators to make fine adjustments to platform height, ensuring workers can position themselves exactly where needed for optimal productivity and safety.
Types and Configurations
Single mast systems offer simplicity and are ideal for smaller-scale projects or situations where space constraints make larger configurations impractical. These units provide excellent flexibility and can be quickly installed and repositioned as work progresses. They’re particularly effective for tasks like painting, minor repairs, or installation work on smaller buildings.
Twin mast systems provide enhanced stability and higher capacity, making them the preferred choice for larger construction projects. The dual mast configuration distributes loads more effectively and can support heavier equipment loads, making them suitable for major facade work, masonry operations, and other demanding applications where multiple workers and substantial materials must be accommodated.
Electric-powered models are increasingly popular for indoor applications and noise-sensitive environments. These units operate quietly and produce no emissions, making them ideal for urban construction projects where noise restrictions apply or for interior work where ventilation might be limited. Electric models also offer precise speed control and smooth operation. The silent operation of an electric Mast Climber is a significant unseen advantage over gas powered Mast climbers.
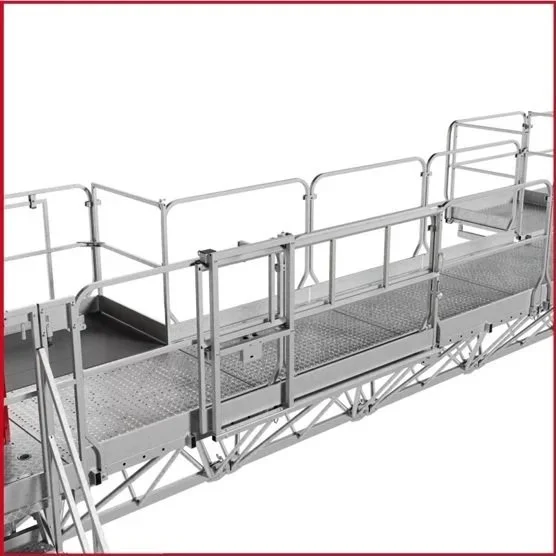
Platform size variations allow contractors to select the optimal configuration for specific tasks. Smaller platforms provide maneuverability in tight spaces, while larger decks can accommodate multiple workers and extensive tool collections. Many manufacturers offer customizable deck configurations that can be tailored to the specific needs of different trades and project requirements.
Multiple decks so several people can work in tandem
Tie-in and anchoring system options vary depending on building construction types. Modern mast climbers can be adapted to work with concrete, steel, masonry, and other structural materials. The anchoring systems are engineered to distribute loads safely while providing the stability necessary for safe operation at height.
Construction Applications and Uses
Building facade work represents one of the most common applications for mast climbers, particularly for window installation, cladding attachment, and exterior finishing operations. The ability to position workers and materials precisely at any height along a building’s exterior makes these platforms invaluable for facade contractors who need efficient access to large vertical surfaces.
Working multiple floors at a time by stacking platforms on towers.
Masonry and bricklaying operations on high-rise construction benefit significantly from the enhanced load capacity that mast climbers provide. Masons can transport heavy materials directly to the work area, eliminating the need for separate material hoists and reducing the time spent moving supplies. The stable platforms allow for precise work even at significant heights.
Bridge maintenance, stadium repairs, and infrastructure projects represent specialized applications where mast climbers excel. Their ability to provide access to challenging locations while supporting the heavy equipment required for structural work makes them an ideal solution for these demanding applications.
Wrapping around a custom facade
Painting, coating, and building restoration work benefit from the consistent platform positioning that mast climbers provide. Workers can maintain optimal working angles and distances from surfaces, resulting in higher quality finishes and improved productivity compared to traditional scaffolding systems.
The customization options run deep
Sign installation and billboard maintenance applications take advantage of the precise positioning capabilities these platforms offer. The ability to make fine height adjustments ensures that installation work can be completed accurately and efficiently, even in challenging wind conditions or tight spaces.
OSHA Safety Requirements and Compliance
OSHA regulation 29 CFR 1926.451 establishes general scaffold requirements that apply specifically to mast climbers, ensuring that these platforms meet the same rigorous safety standards as other scaffolding systems. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for all construction projects using mast climbing work platforms.
Capacity limits, construction standards, and loading specifications are clearly defined to prevent overloading incidents that can lead to equipment failure. Contractors must understand and strictly adhere to manufacturer specifications regarding maximum loads, including personnel, tools, and materials. Exceeding these limits can result in catastrophic failure and serious injuries.
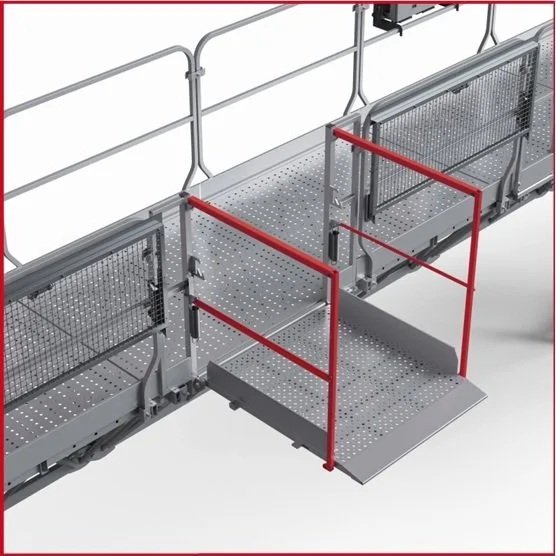
Access requirements and platform clearance regulations specify how workers must safely enter and exit the platform, as well as minimum clearances required around the work area. These standards help prevent falls and ensure that emergency evacuation procedures can be executed safely if necessary.
Ramp options fold out to make it possible to enter and exit a building safely.
Competent person training and supervision mandates require that qualified individuals oversee mast climber operations. These competent persons must understand the equipment’s capabilities and limitations, recognize hazardous conditions, and have the authority to take corrective action when safety violations are observed.
Regular inspection schedules and documentation requirements ensure that equipment remains in safe operating condition throughout the project. Daily inspections must be conducted before use, with comprehensive periodic inspections performed by qualified technicians. All inspection results must be documented and maintained on site.
Fall protection system compliance and guardrail specifications are critical components of mast climber safety. Platforms must be equipped with proper guardrails, and personal fall arrest systems may be required when guardrails are temporarily removed for loading operations or other specific tasks.
Common Hazards and Risk Prevention
Fall risks represent the most serious hazard associated with mast climber operation, particularly when guardrail removal is necessary during loading operations. Workers must use personal fall arrest equipment during these procedures, and strict protocols must be followed to ensure that guardrails are immediately replaced after materials are loaded.
Modern Systems can come with sliding gates as an option.
Training protocols must address all aspects of safe operation, from initial setup through daily use and final disassembly. Comprehensive training programs should cover equipment capabilities, limitations, hazard recognition, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher training helps ensure that safety awareness remains high throughout long-term projects.
Benefits and Advantages Over Traditional Scaffolding
Increased productivity represents one of the most significant advantages that mast climbers offer over conventional scaffolding systems. The ability to quickly reposition the work platform eliminates the time-consuming process of dismantling and rebuilding scaffold sections as work progresses vertically along a building.
Setup time reductions are substantial when comparing mast climbers to traditional scaffolding. While conventional systems require extensive assembly of individual components, mast climbers can be operational in a fraction of the time. This speed advantage translates directly into cost savings and faster project completion times. The space saved on a job site is also significant as are the savings in trucking costs.
Higher load capacity allows mast climbers to transport workers, tools, and materials simultaneously, eliminating the need for separate material hoists in many applications. This capability is particularly beneficial for trades that require substantial amounts of equipment, such as masonry work or mechanical system installation.
Precise elevation positioning enables workers to maintain optimal working positions for extended periods. Unlike fixed scaffolding that may require workers to stretch or work at awkward angles, mast climbers can be positioned to provide ergonomic working conditions that improve both productivity and safety.
Labor cost reductions result from the improved efficiency and reduced setup time that mast climbers provide. Fewer workers are needed for assembly and repositioning compared to traditional scaffolding, and the enhanced productivity means that projects can be completed faster with the same workforce.
Enhanced worker safety, when equipment is properly operated and maintained, stems from the stable platform design and integrated safety systems that modern mast climbers incorporate. The reduced exposure to fall hazards during assembly and disassembly operations contributes to improved overall project safety statistics.
Flexibility for multiple trades makes mast climbers particularly valuable on projects where various contractors need access to the same areas. The ability to quickly adjust platform height and configuration allows different trades to efficiently share the same access equipment, reducing coordination challenges and equipment costs.
FAQ
What training certification is required to operate mast climbing equipment?
OSHA requires that mast climber operators receive training from a competent person who understands the equipment’s operation, hazards, and safety requirements. While no specific federal certification is mandated, many manufacturers provide operator certification programs, and some states have additional requirements. Training must cover equipment inspection, proper loading procedures, emergency operations, and fall protection systems.
How often do mast climbers need to be inspected during a construction project?
Mast climbers must be inspected daily before each use by a competent person, with more comprehensive inspections required periodically based on manufacturer recommendations and project conditions. Any time the equipment is moved, modified, or subjected to unusual conditions (such as severe weather), additional inspections are required before resuming operations.
Can mast climbers be used in windy conditions and what are the weather limitations?
Most mast climbers have specific wind speed limitations, typically requiring shutdown when sustained winds exceed 20-25 mph or gusts reach 35 mph, though exact limits vary by manufacturer and model. Other weather restrictions include ice formation, lightning conditions, and heavy precipitation. Operators must monitor weather conditions continuously and cease operations when conditions exceed safe parameters. A Mast Climber has the advantage of being able to be lowered so wind can be less of a factor for safety.
Elevek Mast Climbers
We can offer Mast Climbers to the North American market from Portugal. Elevek manufactures mast climbers rated at 11,000 lbs and 15,000 lbs. Other access systems like Transport Platforms and Construction Hoists are available as well.